DFT Example Software Implementation
This section demonstrates the implementation of a previously solved example in MATLAB, Python, and C. It reconstructs the input signal - comprising a DC component and two sinusoidal components, computes its Discrete Fourier Transform, analyzes the resulting frequency components (amplitudes and phases), and visualizes the results.
MATLAB#
%% Create Input Signal
% Define input components: DC and two sinusoidal signals
A = [-1 3 2]; % Amplitudes (V)
f = [0 1 3]; % Frequencies (Hz)
phi = [pi/2 pi/4 0]; % Phases (rad)
T = 1; % Signal duration (s)
fs = 8; % Sampling frequency (Hz)
% Create sampled signal
N = T * fs; % Number of samples
n = (0 : N-1)'; % Sample indices
% Initialize signal array
x = zeros(N, 1);
% Construct the signal as a sum of sinusoids
for i = 1 : length(A)
x = x + A(i) * sin(2 * pi * f(i) * n / fs + phi(i));
end
%% Compute DFT
[a, b] = dft(x); % Compute DFT
% Set very small values to 0 to mitigate numerical errors
threshold = 1e-10;
a(abs(a) < threshold) = 0;
b(abs(b) < threshold) = 0;
%% Analyze Frequency Components
Amp = sqrt(a.^2 + b.^2); % Compute amplitude of signal components
Amp(1) = a(1) / 2; % DC component amplitude correction
phase = atan(a./b); % Compute phase (corrected formula)
phase(1) = NaN; % Set DC component phase to NaN
% Frequency axis adjustment for visualization
frq = (-N/2 : N/2-1) / N * fs;
Amp = fftshift(Amp); % Rearrange amplitudes for proper frequency order
phase = fftshift(phase); % Rearrange phases for proper frequency order
%% Plot Amplitude and Phase Spectra
figure;
subplot(2,1,1);
stem(frq, Amp, 'filled');
xlabel('Frequency (Hz)'); ylabel('Amplitude (V)');
title('Amplitude Spectrum'); grid on;
subplot(2,1,2);
stem(frq, phase, 'filled');
xlabel('Frequency (Hz)'); ylabel('Phase (rad)');
title('Phase Spectrum'); grid on;
%% DFT Function Implementation
function [a, b] = dft(x)
% Compute the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of a real input signal
N = length(x); % Number of samples
n = 0 : N-1; % Sample indices
phi = 2 * pi * (n' * n) / N; % Compute angles for DFT matrix
% Compute cosine and sine frequency components
a = (2 / N) * cos(phi) * x;
b = (2 / N) * sin(phi) * x;
end
Python#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create Input Signal
# Define input components: DC and two sinusoidal signals
A = np.array([-1, 3, 2]) # Amplitudes (V)
f = np.array([0, 1, 3]) # Frequencies (Hz)
phi = np.array([np.pi/2, np.pi/4, 0]) # Phases (rad)
T = 1 # Signal duration (s)
fs = 8 # Sampling frequency (Hz)
# Create sampled signal
N = int(T * fs) # Number of samples
n = np.arange(N) # Sample indices
# Initialize signal array
x = np.zeros(N)
# Construct the signal as a sum of sinusoids
for i in range(len(A)):
x += A[i] * np.sin(2 * np.pi * f[i] * n / fs + phi[i])
# Compute DFT
def dft(x):
""" Compute the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of a real input signal. """
N = len(x)
n = np.arange(N).reshape(1, N) # Create row vector
phi = 2 * np.pi * n.T * n / N # Compute angles for DFT matrix
# Compute cosine and sine frequency components
a = (2 / N) * np.dot(np.cos(phi), x)
b = (2 / N) * np.dot(np.sin(phi), x)
return a, b
a, b = dft(x) # Compute DFT
# Set very small values to 0 to mitigate numerical errors
threshold = 1e-10
a[np.abs(a) < threshold] = 0
b[np.abs(b) < threshold] = 0
# Analyze Frequency Components
Amp = np.sqrt(a**2 + b**2) # Compute amplitude of signal components
Amp[0] = a[0] / 2 # DC component amplitude correction
phase = np.arctan(a/b) # Compute phase (corrected formula)
phase[0] = np.nan # Set DC component phase to NaN
# Frequency axis adjustment for visualization
frq = np.fft.fftfreq(N, d=1/fs) # Compute frequency axis
frq = np.fft.fftshift(frq) # Rearrange for plotting
Amp = np.fft.fftshift(Amp) # Rearrange amplitudes
phase = np.fft.fftshift(phase) # Rearrange phases
# Plot Amplitude and Phase Spectra
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
markerline, stemline, baseline = plt.stem(frq, Amp, linefmt='b', markerfmt='bo', basefmt="k-")
plt.xlabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude (V)')
plt.title('Amplitude Spectrum')
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
markerline, stemline, baseline = plt.stem(frq, phase, linefmt='r', markerfmt='ro', basefmt="k-")
plt.xlabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.ylabel('Phase (rad)')
plt.title('Phase Spectrum')
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
C#
The C code was developed using the Code::Blocks IDE as a Console Application. The results are stored in .dat files, which can be visualized using GNUplot for analysis and comparison.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI 3.14159265358979323846
#define FS 8 // Sampling frequency (Hz)
#define T 1 // Signal duration (s)
//#define N (FS * T) // Number of samples
// DFT Function
void dft(double x[], double a[], double b[], int N) {
// Compute DFT of a real input signal
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
a[k] = 0.0;
b[k] = 0.0;
for (int n = 0; n < N; n++) {
double phi = 2 * PI * k * n / N;
a[k] += (2.0 / N) * x[n] * cos(phi);
b[k] += (2.0 / N) * x[n] * sin(phi);
}
}
}
// FFT Shift (Rearrange Frequency Components)
void fftshift(double arr[], int N) {
int half = N / 2;
double temp;
for (int i = 0; i < half; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i + half];
arr[i + half] = temp;
}
}
int main() {
int N = FS * T; // Number of samples
int L; // Number of input signals
// Define input components: DC and two sinusoidal signals
double A[] = {-1, 3, 2}; // Amplitudes (V)
double f[] = {0, 1, 3}; // Frequencies (Hz)
double phi[] = {PI/2, PI/4, 0}; // Phases (rad)
double x[N]; // Sampled signal array
double a[N], b[N]; // DFT cosine and sine coefficients
double Amp[N], phase[N], frq[N]; // Amplitude and phase spectra
// Generate sampled signal
L = sizeof(A) / sizeof(A[0]);
for (int n = 0; n < N; n++) {
x[n] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < L; i++) {
x[n] += A[i] * sin(2 * PI * f[i] * n / FS + phi[i]);
}
}
// Compute DFT
dft(x, a, b, N);
// Eliminate very small numerical errors
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
if (fabs(a[k]) < 1e-10) a[k] = 0;
if (fabs(b[k]) < 1e-10) b[k] = 0;
}
// Compute amplitude and phase spectra
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
Amp[k] = sqrt(a[k] * a[k] + b[k] * b[k]); // Magnitude
if (k == 0) {
Amp[k] = a[k] / 2; // DC component correction
phase[k] = 0; // DC phase is undefined
} else {
if (b[k] == 0) {
phase[k] = 0; // Division by 0
} else {
phase[k] = atan(a[k]/b[k]); // Compute phase
}
}
}
// Frequency axis
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
frq[k] = ((k - N / 2) * FS) / (double)N;
}
// Apply FFT Shift to rearrange amplitude and phase spectra
fftshift(Amp, N);
fftshift(phase, N);
// Print results
printf("Amplitude values:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("Amplitude[%d] = %f\n", i, Amp[i]);
}
printf("\nPhase values:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("Phase[%d] = %f\n", i, phase[i]);
}
printf("\nFrequencies:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("Frequency[%d] = %f\n", i, frq[i]);
}
// Save data to files for later visualization
FILE *amp_file = fopen("amplitude_spectrum.dat", "w");
FILE *phase_file = fopen("phase_spectrum.dat", "w");
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
fprintf(amp_file, "%lf %lf\n", frq[k], Amp[k]);
fprintf(phase_file, "%lf %lf\n", frq[k], phase[k]);
}
fclose(amp_file);
fclose(phase_file);
// visualize
printf("\nUse GNUplot to visualize:\n");
printf("gnuplot -e \"plot 'amplitude_spectrum.dat' with linespoints title 'Amplitude Spectrum'\"\n");
printf("gnuplot -e \"plot 'phase_spectrum.dat' with linespoints title 'Phase Spectrum'\"\n");
return 0;
}
Visualization
- Open command prompt (Windows)
- Check if GNUplot is installed using:
- Navigate to the folder with '.dat' files using 'cd' command:
- If the folder is on a different drive (e.g., D:), first switch to that drive:
- Verify the files exist by listing them:
- Open GNUplot by running:
- To plot the Amplitude Spectrum, type inside the GNUplot interface:
- To plot the Phase Spectrum, type inside the GNUplot interface:
- To plot both graphs in one window:
- To save the Amplitude Spectrum in the current directory, type inside the GNUplot interface:
- To exit GNUplot, type:
where gnuplot
or
gnuplot --version
If GNUplot is not installed, download and install it, ensuring the "Add to system PATH" option is selected during installation.
cd C:\path\to\your\folder
Replace 'C:\path\to\your\folder' with the actual folder path.
D:
cd path\to\your\folder
dir
gnuplot
This should open the GNUplot command-line interface.
set xlabel 'Frequency (Hz)'
set ylabel 'Amplitude (V)'
set grid
plot 'amplitude_spectrum.dat' with impulses title 'Amplitude Spectrum'
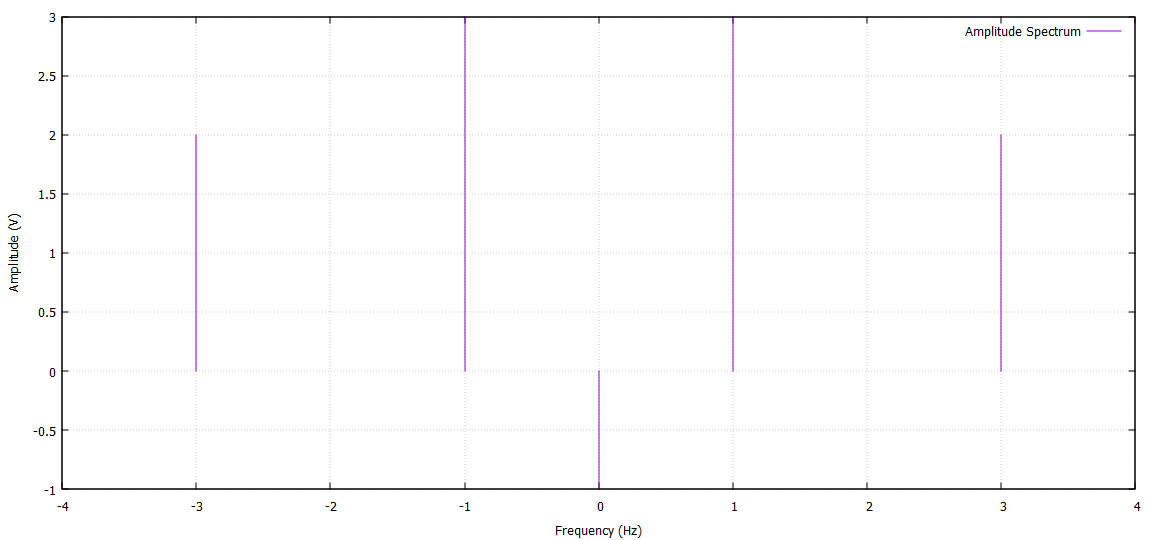
set xlabel 'Frequency (Hz)'
set ylabel 'Phase (rad)'
set grid
plot 'phase_spectrum.dat' with impulses title 'Amplitude Spectrum'
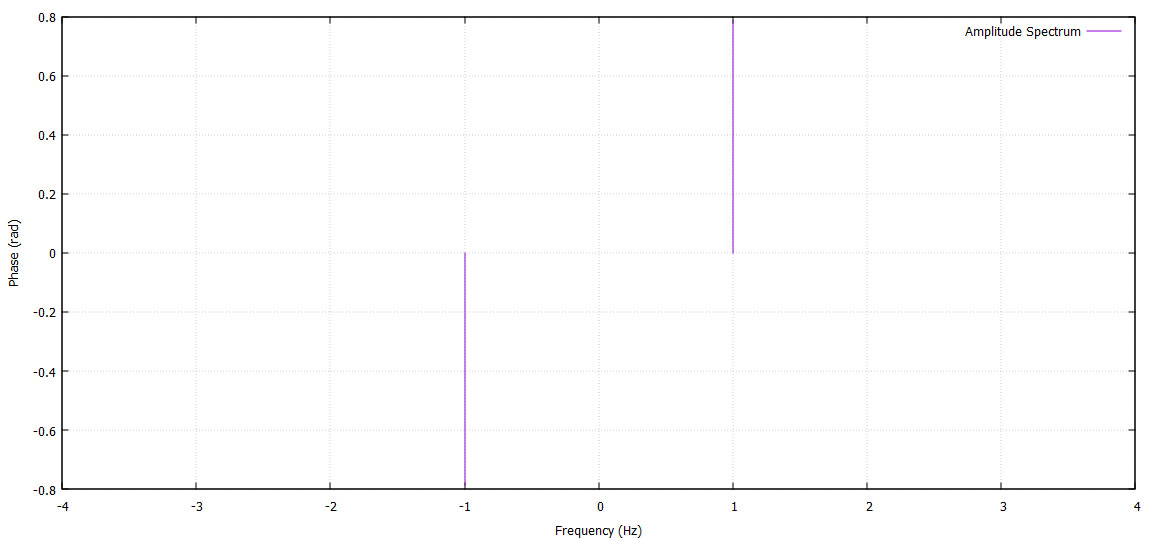
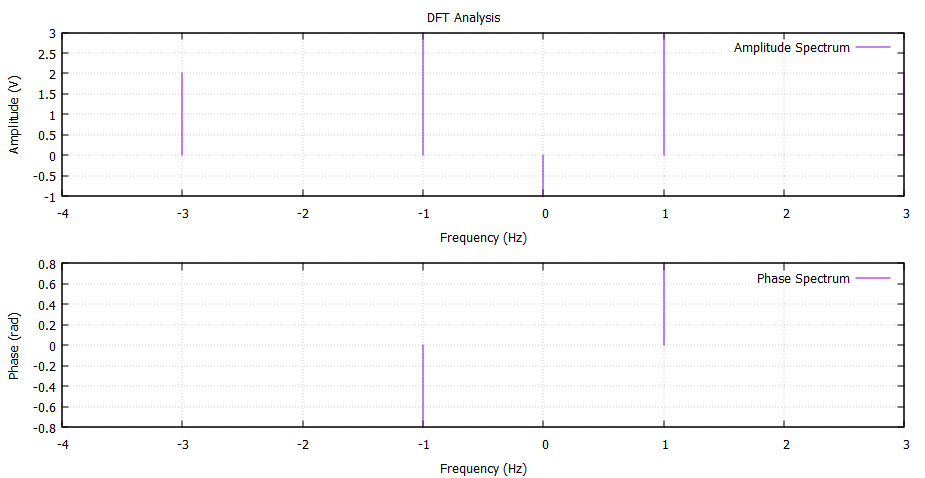
set multiplot layout 2,1 title "DFT Analysis"
set xlabel 'Frequency (Hz)'
set ylabel 'Amplitude (V)'
set grid
plot 'amplitude_spectrum.dat' with impulses title 'Amplitude Spectrum'
set xlabel 'Frequency (Hz)'
set ylabel 'Phase (rad)'
set grid
plot 'phase_spectrum.dat' with impulses title 'Phase Spectrum'
unset multiplot
set terminal png
set output 'amplitude_spectrum.png'
set xlabel 'Frequency (Hz)'
set ylabel 'Amplitude (V)'
set grid
plot 'amplitude_spectrum.dat' with impulses title 'Amplitude Spectrum'
set output
quit